Simulation
Objective:
The simulation allows the gain of development specifications in early stages of the design and behavior of a component or group of components. This reduces the experimental effort and development time.
Overview of simulation tools:
1D hydraulic calculation
AMESim (LMS)
- Modules:
- Signal processing
- Mechanics
- Hydraulic
- Pneumatics
- Engine cooling system
- Electromechanical Systems
- Thermal Systems
and custom applications calculation and design of diesel injection systems or components
|
1D worker process account
PROMO, Boost (AVL)
- Review of the charge cycle
(Volumetric efficiency, residual gas content, efficiency)
- Thermodynamic analysis
- Component design / dimensioning
(Saugrohrlängenauslegung, tank, exhaust system, charging)
|
|
0D worker process account
Matlab-Simulink
- Review of the charge cycle
(Volumetric efficiency, residual gas content, efficiency) without wave transit times
- Combustion simulation (HCCI)
|
3D flow calculation
FIRE (AVL)
- spatially and temporally resolved flow fields
- Mixture formation
- Combustion
- Coupling with 1D programs
- some automatic mesh generation
- modular design -> Integration of subroutines
|
Examples:
1D hydraulic calculation AMESim (LMS) Unit Injector
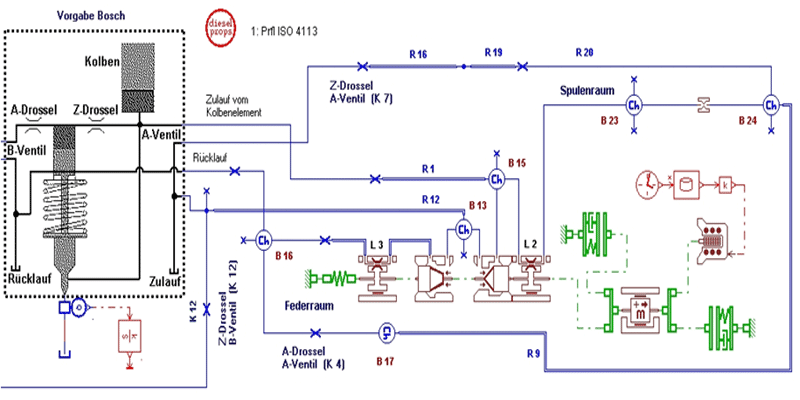
Model: Detail of a total hydraulic model to calculate the flow through a solenoid valve
Target: Design of throttle diameter for regulating the temperature of the solenoid valve
3D flow calculation - Fire - charge movement with static flow.








